
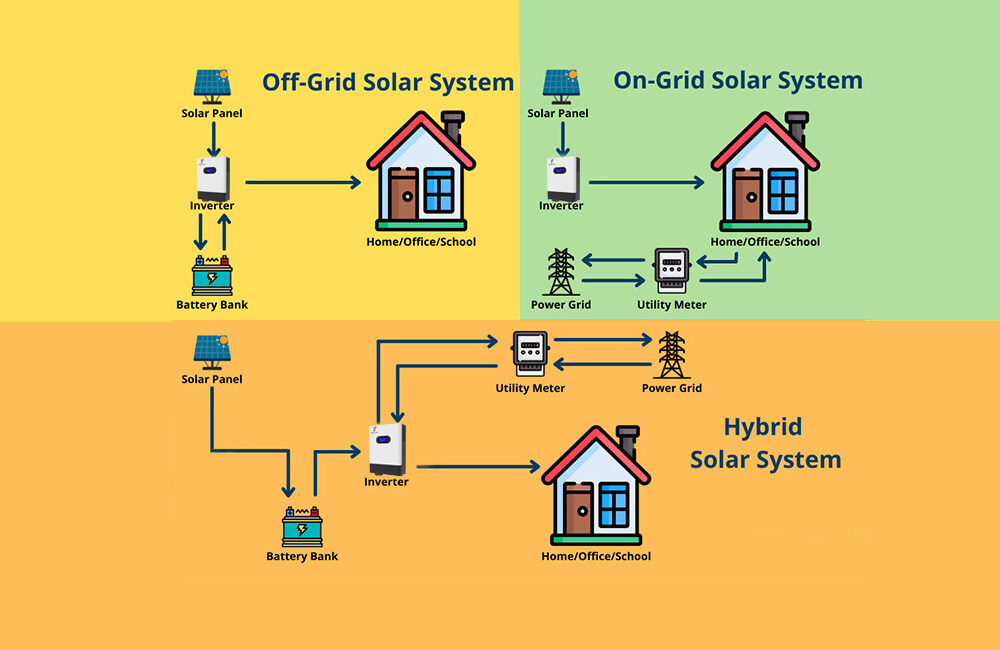
Solar power systems have gained significant popularity in recent years as a sustainable and cost-effective energy solution. Central to these systems are inverters, which play a crucial role in converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) electricity. However, not all inverters are created equal. In this blog, we will explore the differences between off-grid, on-grid, and hybrid inverters, helping you understand which one is best suited for your specific needs.
Off-Grid Inverters:
Off-grid inverters, also known as standalone inverters, are designed for systems that operate independently of the utility grid. These inverters are commonly used in remote areas where grid access is limited or in situations where individuals seek complete energy independence. Off-grid inverters convert the DC power generated by solar panels, batteries, or other renewable energy sources into AC power for immediate consumption or storage in batteries. By working in conjunction with battery banks, off-grid systems ensure a reliable power supply during periods of low solar generation or in the event of a power outage. Off-grid inverters provide users with autonomy from the utility grid and are highly reliable in areas with frequent power outages or remote locations with limited grid access.
On-Grid Inverters:
On-grid inverters, also referred to as grid-tied inverters, are designed to work in conjunction with the utility grid. These inverters are connected to the electrical grid and synchronize the solar power system with it. The primary function of on-grid inverters is to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into usable AC power for immediate consumption. Excess electricity produced by the solar system is fed back into the grid, allowing users to earn credits or compensation through net metering. Unlike off-grid inverters, on-grid systems do not require battery storage as their focus is primarily on reducing electricity bills and contributing to a greener environment.
Hybrid Inverters:
Hybrid inverters combine the features of both off-grid and on-grid inverters, providing users with greater flexibility and reliability. These inverters are designed for systems that have the capability to operate both off-grid and on-grid. Hybrid inverters can convert DC power from solar panels into AC power for immediate consumption, store excess energy in batteries for later use, and also synchronize with the utility grid when necessary. This versatility allows users to enjoy the benefits of energy independence while still having the option to connect to the grid and take advantage of net metering. Hybrid systems are becoming increasingly popular as they provide greater flexibility and reliability in areas with intermittent grid access or frequent power outages.
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between off-grid, on-grid, and hybrid inverters is essential when selecting the right inverter for your solar power system. Off-grid inverters offer complete energy independence and reliability, making them ideal for remote areas or as backup power solutions. On-grid inverters focus on reducing electricity bills and contributing to a greener environment by synchronizing with the utility grid. Hybrid inverters provide the best of both worlds, allowing users to enjoy the benefits of off-grid independence while still having the option to connect to the grid. Consider your energy requirements, location, and desired level of independence to make an informed decision and maximize the benefits of your solar energy system.
6-20 个字符(仅限字母加数字)
密码不一致